Arthritis is a condition that affects the joints in the body. Arthritis can cause significant joint pain that affects your quality of life. If you have been diagnosed with arthritis, seemingly simple tasks like opening a jar may be extremely difficult. Though there is no cure for arthritis, there are many effective treatment options for managing arthritis pain and minimizing symptoms.
Read on to find out what you need to know about managing arthritis pain.
Types of Arthritis
Arthritis is extremely common. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that nearly a quarter of American adults have been diagnosed with arthritis. (1)
So, what are the different forms of arthritis? Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are the most common types of arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis and autoimmune disease. The condition is a rheumatic disease, meaning it develops as a result of immune system dysfunction. On the other hand, osteoarthritis develops as a result of repeated injury and use, and subsequent joint damage. For example, osteoarthritis is more common among athletes.
Other, less common forms of arthritis include:
- Gout: This type of arthritis develops as a result of the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Symptoms are most often experienced in the big toe.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Psoriatic arthritis is connected to psoriasis and is caused by immune system dysfunction.
- Ankylosing spondylitis: This form of arthritis is extremely rare and primarily affects the spine. Ankylosing spondylitis can cause back pain and stiffness.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Keep in mind that different types of arthritis may be accompanied by different symptoms.
Some of the main symptoms of arthritis include:
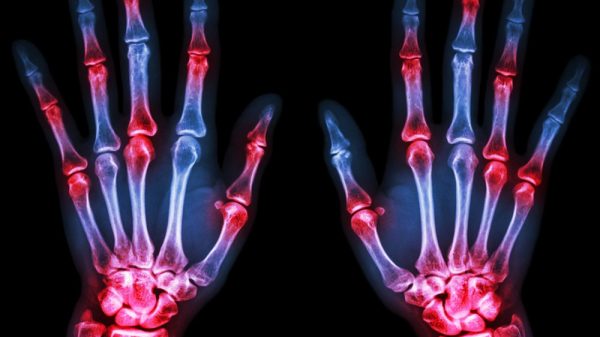
- Joint stiffness: Typically, stiffness will be felt in the joints, particularly in the larger joints of the fingers and toes. Stiffness tends to be the worst in the morning and gradually improves as the day progresses.
- Swelling: Finger and toe joints may appear to be swollen and misshapen.
- Redness: Redness in the joint area may accompany swelling.
- Pain: Joint pain is a very common and often debilitating symptom of arthritis.
- Limited range of motion: Swelling and pain in arthritic joints can have a serious impact on your ability to move your joints. It is difficult to move a painful joint.
Symptoms Specific to Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Fatigue: Because rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory condition that impacts the immune system, symptoms are not always restricted to the joints. Inflammation can be systemic, causing fatigue and exhaustion.
- Flu-like symptoms: It’s not uncommon for rheumatoid arthritis to also be accompanied by fever, chills, and body aches. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, these symptoms are the result of systemic inflammation that irritates body tissues and causes more generalized symptoms.
Managing Arthritis Pain
Pain relief and management are key to living and thriving with arthritis. There are many strategies and treatments that can help relieve arthritis pain and improve your quality of life. Keep in mind that these suggestions apply primarily to the most common types of arthritis: rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Dietary changes can help manage systemic inflammation, in turn helping to control joint inflammation and pain. So, what are some dietary changes you can make as part of your arthritis pain management plan?
Fruits and Veggies
First of all, it’s important to ensure that you’re eating plenty of fruits and vegetables. Fruits and veggies are packed with micronutrients including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. All of these micronutrients help the body carry out biological processes smoothly. Antioxidants play a particularly important role in managing inflammation and oxidative stress. Antioxidants are small particles that neutralize free radicals, helping to minimize cellular damage and support immune system health.
High-Quality Protein
Next, make sure you’re getting plenty of high-quality protein that offers optimal ratios of essential amino acids. Arthritis may be linked to imbalances in essential amino acids. (2) Research shows that certain essential amino acids like tryptophan, methionine, and phenylalanine may function as anti-inflammatory agents. (2) Moreover, arthritis is often associated with sarcopenia, which is the loss of muscle mass. (2)
It’s important to get plenty of high-quality protein or supplements that offer balanced ratios of essential amino acids. Getting optimal ratios of essential amino acids may help manage inflammation while also restoring muscle mass.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are packed with fiber, which feeds the healthy bacteria populating the gut. When good bacteria feed on fiber, they produce anti-inflammatory byproducts that travel throughout the body and help reduce inflammation. Excellent sources of whole grains include quinoa, millet, brown rice, oats, whole-grain bread, and whole-grain pasta.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats also play an important role in reducing inflammation and mitigating symptoms associated with arthritis. In particular, omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats that are linked to lower levels of inflammation. Sources of healthy fat to incorporate into your diet include nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Minimizing Junk Foods
Several unhealthy foods are linked to inflammation and worsening arthritis symptoms. Steer clear of these foods to protect your arthritic joints:
- Refined grains, like white bread, white pasta, and pastries
- Added sugars found in candy, ice cream, and breakfast cereal
- Saturated fat from fatty cuts of meat and full-fat dairy
- Processed and packaged food products
2. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Medication may be a helpful way to manage pain associated with arthritis. Over-the-counter pain medications like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are often used to manage arthritis pain. Ibuprofen works to reduce inflammation in the joints, therefore reducing pain.
Acetaminophen is another medication option available at your local grocery store or pharmacy that can help manage arthritis pain. Always follow directions when taking medications to minimize side effects. For example, taking too much acetaminophen can result in serious liver damage.
3. Prescriptions Medications
In addition to over-the-counter pain relievers, your physician may prescribe certain medications to help manage arthritis symptoms and pain. One class of medications is called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, which help manage rheumatoid arthritis. These immunosuppressant medications, known as DMARDs, work by decreasing immune system activity. The immune system is therefore unable to continue launching attacks against the body, which helps relieve pain associated with arthritis. Because DMARDs address the root cause of rheumatoid arthritis – inflammation – they are generally used to control the disease for a long period of time.
Corticosteroids like prednisone may also be prescribed for fast relief from inflammatory symptoms associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Unlike DMARDs, they are not usually appropriate to use over a long period of time and are used to manage acute episodes of arthritis pain.
3. Regular Exercise and Increasing Muscle Mass
Strengthening your muscles can take pressure off the entire musculoskeletal system. Keep in mind that if you have rheumatoid arthritis, it’s also likely that you are experiencing muscle loss or sarcopenia. Taking intentional steps to increase physical activity and increase muscle mass can help support your joints and alleviate symptoms. Strength training combined with essential amino acid supplementation can help restore lean muscle mass and play a role in alleviating arthritis symptoms.
Stretching can also help support the strength of ligaments, tendons, and other connective tissues surrounding joints. Physical therapy is also an excellent option for individuals with impaired movement from arthritis.
4. Weight Loss
Obesity can exacerbate arthritis since extra weight puts extra pressure on the joints. Losing weight is an effective strategy for relieving joints of pressure. Moreover, carrying extra weight may also be linked to inflammation. Striving to reach a healthy weight, combined with lifestyle changes and an anti-inflammatory diet may help manage arthritis symptoms.
5. Surgery
In serious cases, arthritis can completely render joints unusable. In these cases, your doctor may recommend undergoing joint replacement surgery, such as knee replacement surgery. Joint replacements are usually recommended only in severe cases of osteoarthritis.
Things to Keep in Mind
If you are experiencing joint pain, it’s crucial to reach out to your health care provider. Your physician will evaluate your symptoms and create a treatment plan that works for your specific needs. Specialists in rheumatology, or rheumatologists, can help you create a tailored treatment plan for your case of arthritis. Depending on the type of arthritis you have, you may also see other specialists.
Conclusion: Tips and Strategies for Managing Arthritis Pain
Arthritis pain may be severe and can negatively affect your quality of life and ability to participate in activities that you enjoy. Though there is no cure for arthritis, there are steps you can take to minimize arthritis pain and symptoms. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in antioxidants and essential amino acids, getting regular exercise, and taking medications for pain management are a few strategies that can manage arthritis, mitigate chronic pain, and subsequently improve your quality of life.

References:
(1) https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/data_statistics/national-statistics.html