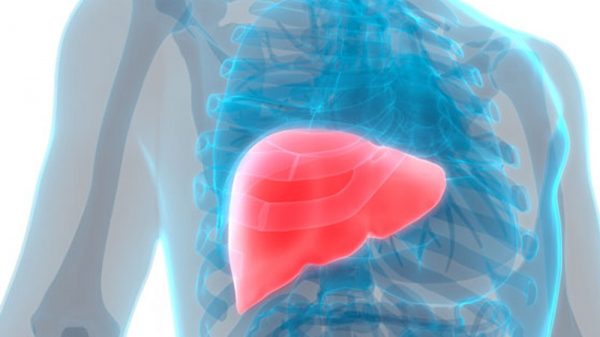
There are two common genetic liver diseases, alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, and hemochromatosis. Hemochromatosis is a condition that occurs when a deposit is collected in somebody’s organs like the liver. In the United States, the primary hemochromatosis form is more common among people. About one out of every two hundred people have hemochromatosis. When a family member has hemochromatosis, the parents, children, and siblings will be at risk. The secondary hemochromatosis form is not genetic but is caused by some other diseases like thalassemia. Thalassemia is the genetic blood disease that results in anemia. The overload of iron connected with hemochromatosis is said to affect males more than females. During their menstruation, women lose blood and will unlikely show iron overload signs until they are passed menopause. Hemochromatosis is common among those in Western Europe.
There are some hemochromatosis metabolic disorder symptoms like joint pain, liver disease, unexplained loss of weight, fatigue, skin darkening known as bronzing, pain in the abdomen, and absence of sexual desire.
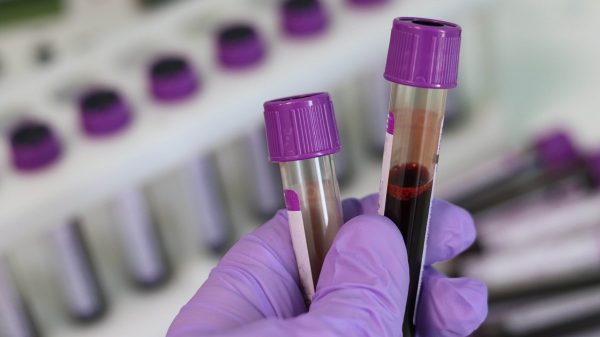
Those with this condition may show heart disease and diabetes signs and may develop testicular atrophy, cirrhosis, infertility, and liver cancer. Hemochromatosis is diagnosed thru blood tests, if they discover excess iron, then another blood test may be carried out. These tests may also be conducted on the patient’s family members.
Hemochromatosis Treatment
The treatment goal here is to get rid of the excess iron in the body. It also reduces complications or symptoms that come with the disease. The process of removing this excess iron is called phlebotomy during, which a certain amount of blood is extracted weekly for two to three years. It will usually last until the buildup of iron is reduced.
Phlebotomies will be needed less after the initial treatment, but its frequency differs based on the circumstances of the individual.
The therapy of iron chelation is another type of treatment. This procedure makes use of medicine to get rid of the excess iron, and this is a better approach for those who can not go through routine blood extraction.
The medications used in iron chelation are either taken orally or injected. You can do this at your doctor’s clinic or oral treatment at home. To keep the level of your iron down, these people should stay away from iron, especially vitamins preparations. Health care providers usually help plan the diet of their hemochromatosis patients.
Other Genetic Liver Conditions
Asides hemochromatosis, there are other types of liver conditions. For example, we have the immune liver disorder and polycystic liver disease.
Immune liver disorder is also known as autoimmune hepatitis. It is an inflammation of the liver, which happens when the body’s immunity goes against the liver cells. There is no known cause of this disorder, but environmental and genetic factors overtime may trigger the disease.
The untreated autoimmune liver conditions can result in liver scarring and could eventually cause liver failure. Early diagnosis will help in treating this condition. Some drugs can suppress your immune system. In severe cases, a liver transplant may need to be carried out.
Symptoms and signs of this condition differ amongst persons and can happen suddenly. There are people with unidentified problems during the early stages whereas, some experience symptoms and signs that could include abdominal discomfort, fatigue, enlarged liver, whites and skins of the eyes yellowing, joint pains, menstrual periods loss, skin rashes.
If you have any of these symptoms, go see a doctor. Autoimmune hepatitis happens when the body’s immunity naturally attacks bacteria, viruses, and other types of pathogens start to target your liver.
This attack may result in chronic inflammation and could seriously damage the cells of the liver. It is still unclear why this happens, but researchers are thinking, autoimmune hepatitis is triggered by gene interaction responsible for immune system function control and the exposure to a particular drug or virus.
Polycystic Liver Disease
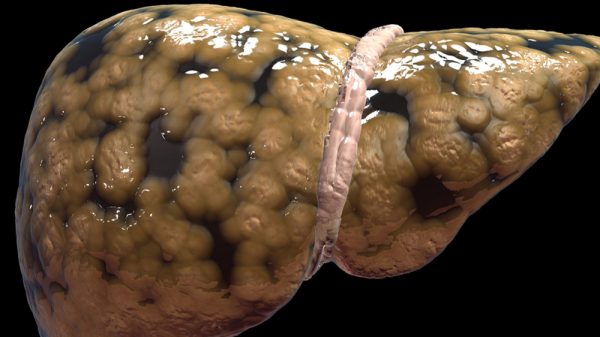
This condition is rare, and it causes fluid-filled sacs or cysts that grow through the liver. Normally, a liver has a smooth uniform like appearance, but a plastic liver will look like large grape clusters. These cysts grow separately in the liver parts. It may get large or too numerous and cause health complications or discomfort.
However, those with polycystic liver conditions may not show symptoms and can have a normal life. Most people with this condition inherited it, but there is no certain genetic link to the disease. Women are thought to be affected by it more than men. Also, those with polycystic kidney disease are commonly affected, and its frequency increases with the advanced renal condition and increasing age.
People with this condition usually do not find out about it until they become adults. By this age, the cysts have grown large enough and are easily detected. The size of the cyst varies. It’s respective of the cyst size or numbers, the liver will continue functioning, and thus this disease may not be life-threatening.
Since this condition is usually inherited, the immediate families with this disease should go for a test. Diagnosis of polycystic liver disease is made from imaging tests like MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound.
Most people with these conditions do not show symptoms. But if their liver gets bulky and enlarged with the cysts, then symptoms might appear. These symptoms include abdominal pain, abdominal swelling or bloating, feeling of fullness, breath shortness.
Other complications that may be noticed are cyst bleeding, cyst infection, jaundice, and obstruction of the bile duct. Treatment for this condition will not be needed until symptoms begin to show.
Mild pain may be treated with some medications, but if there are significant complications or discomfort, there are different options for treatment.
The genetic liver disease varies, and the symptoms and conditions also differ.