What are the final stages of cirrhosis of the liver? You might have heard about the different stages of some particular diseases and how people are being described as being in the last stage of the disease. This is usually the case of the terminal or chronic condition of which cirrhosis is a part. In this article, you will get to understand the condition, cirrhosis, its different stages, symptoms, and causes. This is a condition that arises from liver disease complications and it involves liver cells loss and liver scarring which is irreversible.
Cirrhosis is caused by hepatitis B (viral) and alcohol, although several other causes exist these are the most common. The effect of cirrhosis on the body includes weakness, lack of appetite, fatigue, itching, easy bruising, and jaundice. There are several methods of diagnosis cirrhosis such as conducting a physical examination, blood tests, and historical examination. A lot of complications can proceed from cirrhosis. For example, a person with cirrhosis might begin to have abdominal swelling, variceal bleeding, hepatorenal syndrome, liver cancer, hypersplenism, and hepatic encephalopathy. This is just a brief introduction to cirrhosis, now let’s dig in deeper.
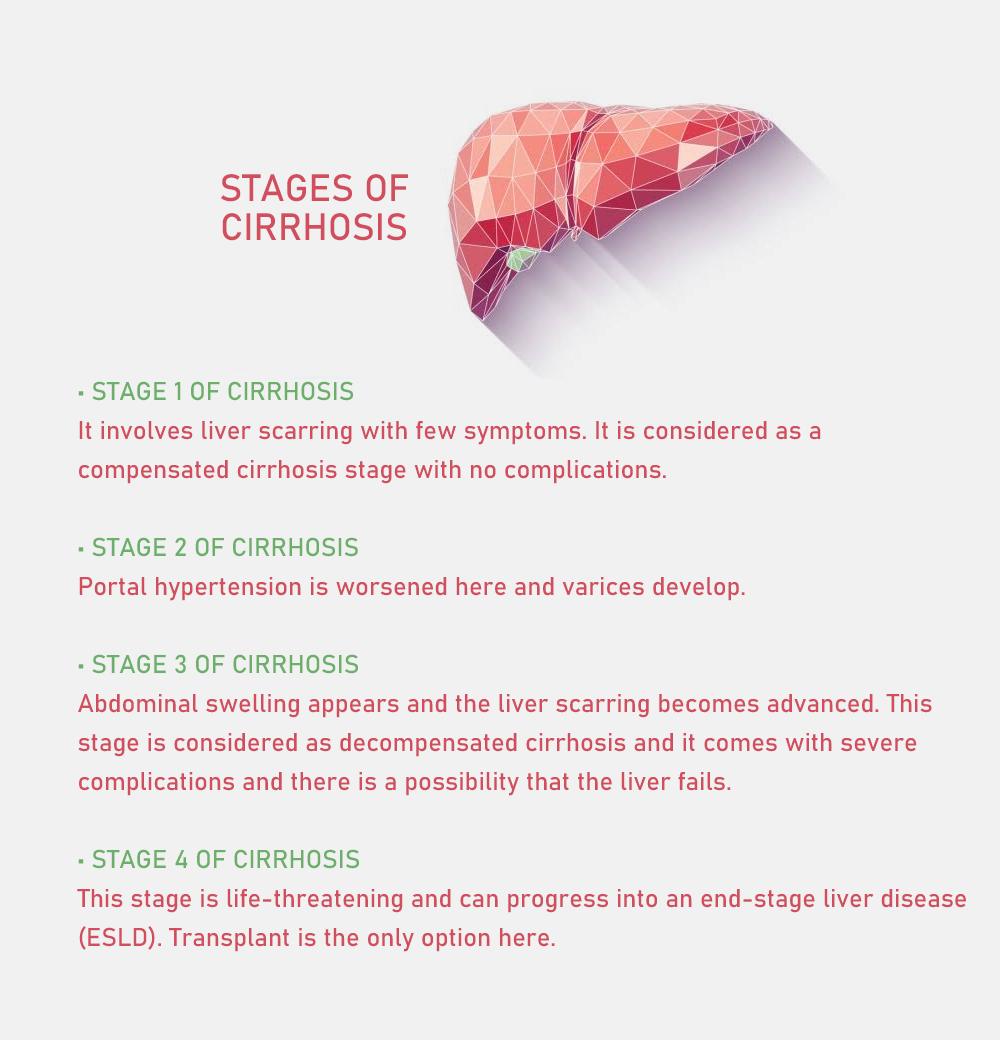
Cirrhosis Progression
An abnormally structured and functioning liver can cause complications like cirrhosis. The reason why this liver disease results in cirrhosis is that they kill and damage liver cells. The attempt of the liver to repair itself can cause the formation of scar tissues. The surviving liver cells try to replenish the dead cells by multiplying. This often leads to clusters of new liver cells known as regenerative nodules in the scarred tissue.
A lot of things are listed as causing cirrhosis, such as fat, alcohol, certain medications, toxic metals, viruses, etc.
The importance of the liver in the body cannot be overemphasized. The liver performs vital roles within the body for example, the production of certain substances like clotting protein proteins that are needed for blood clotting. The liver also regulates the body’s supply of lipids and sugar that is used as a source of fuel. If the liver is going to carry out these roles then it has to be functioning normally. It should also be close to the bloodstream as the substances are transported through the bloodstream.
During cirrhosis, the unique relationship between the blood and liver is severed thus the livers would not have the ability to remove and producing theses substances. The scarring will also obstruct blood flow through the cells of the liver and the liver itself. Due to this, blood builds up within the portal vein causing increased pressure, this condition is known as portal hypertension.
Symptoms of Cirrhosis
Individuals with cirrhosis experience little symptoms of liver conditions or none. Some symptoms might be nonspecific. Common examples of the symptoms include
- Jaundice (yellow skin as a result of blood bilirubin accumulation)
- Fatigue
- Lack of appetite
- Weakness
- Easy bruising
- Itching
What Are The Final Stages Of Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis on its own is already the I signal that the liver damage has entered into a late stage. The early stages are characterized by liver inflammation, untreated inflammation can cause scarring (fibrosis). the liver can still heal at this point if adequate treatment is administered. But if fibrosis is left untreated it progresses into cirrhosis.
At this cirrhosis stage, it becomes impossible to heal the scarred tissue, the only thing that can be done here is to prevent or slow down its progression. Cirrhosis patients may develop complication signs of end-stage liver disease (ESLD). the only possible treatment here is to conduct a liver transplant.
- Stage 1 of cirrhosis: It involves liver scarring with few symptoms. It is considered as a compensated cirrhosis stage with no complications.
- Stage 2 of cirrhosis: Portal hypertension is worsened here and varices develop.
- Stage 3 of cirrhosis: Abdominal swelling appears and the liver scarring becomes advanced. This stage is considered as decompensated cirrhosis and it comes with severe complications and there is a possibility that the liver fails.
- Stage 4 of cirrhosis: This stage is life-threatening and can progress into an end-stage liver disease (ESLD). Transplant is the only option here.
Cirrhosis Complications
Here are some of the complications that may arise from liver cirrhosis.
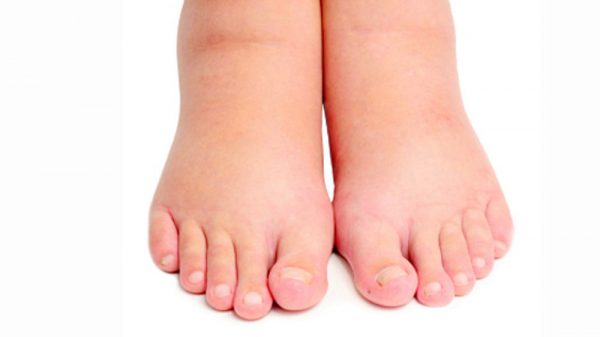
Ascites and Edema complications
With the progression of cirrhosis, kidney receive signals to retain the body’s water and salt. The excess water and salt are first accumulated in the skin tissues below legs and ankles due to gravity’s effect when sitting or standing. This condition is known as pitting edema or peripheral edema. Time fluid may also build up in the cavity of the abdomen (ascites) and this will lead to abdominal swelling, increased weight, and abdominal discomfort.
Esophageal variceal bleeding
The scarred tissue prevents blood flow from the person’s intestine back to the receiving point In the heart. This increases portal vein’s pressure referred to as portal hypertension. As this pressure increases it allows the lower pressure veins from the liver to enter the heart. These veins are the ones that line the stomach’s upper part and the esophagus lower part.
The result of this bypass causing increased pressure in these veins as they expand and this condition is known as gastric varices and esophageal varices. The varices increase based on how high the pressure in the portals are and would most likely cause the patient to bleed into the stomach or esophagus via the veins.
In Conclusion
Knowing what are the final stages of cirrhosis of the liver is very essential in order to follow up on the condition. But it is better to arrest the situation while it is still in its early stage when it can still be treated without the need for replacing the liver.