Let’s get right down to the medical workings for cirrhosis labs in this article. First, let’s recap the specific condition. Cirrhosis would be the condition by which the liver will be scarred and entirely affected. Scar tissue formation takes the place of healthy liver tissues when it has gotten to the point of really ill, then prevents the liver from performing normally. When the cirrhosis gets even much, the liver starts to fail. Cirrhosis includes many signs or symptoms, such as for example, fatigue to extremely itchy skin. These indications may not come about until a patient’s liver becomes badly affected. Factors consist of alcoholic disease of the liver, nonalcoholic fatty disease of the liver, chronic hepatitis B, and lastly, chronic hepatitis C.
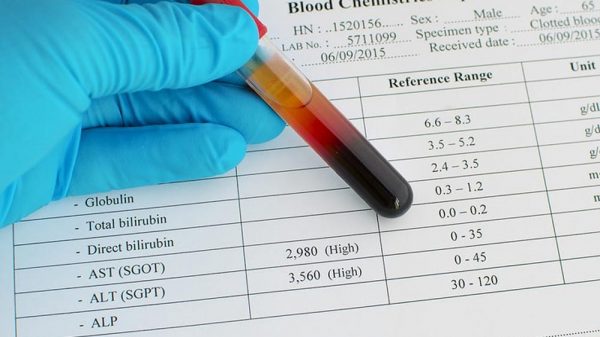
Physicians diagnose cirrhosis according to a patient’s medical background, a physical assessment, in addition to test findings. Tests entail blood tests such as for instance, liver function examinations, and several testings for viral infection, liver biopsy, to imaging tests. For starters, the physical exam would mean the doctor will observe how the liver of the patient feels, and how big it really is (a cirrhotic affected liver will be irregular and bumpy as opposed to normally being smooth). Next: blood testing. in case of the doctor prospects cirrhosis, you’re going to be provided blood tests to test if there is a presence of liver disease. Other examinations in some instances is required to take visuals associated with the liver, such as for example ultrasound or CT scan. Another would be a biopsy. Biopsies will imply the doctor might wish to confirm a diagnosis after taking a patient’s sample (this is known as the biopsy process) coming from the liver. And finally, there is surgery. In some cases, cirrhosis will be diagnosed during the course of the surgery itself, just as soon as the doctor already can peer into the liver completely. This particular liver can also be examined by using a laparoscope. This is a type of viewing device which is inserted through a small incision into the abdomen. Need to learn more? Keep reading to get a more detailed understanding of cirrhosis labs.
Cirrhosis Labs: What Goes on in Cirrhosis Tests
Identifying the presence of cirrhosis is really important for virtually any patient having this chronic type of liver disease. Generating the precise diagnosis for cirrhosis is going to influence management as well as follow-up of the condition.
Being the final-stage of every chronic type of liver disease, like hepatitis B or hepatitis C, excessive alcohol usage disorder complications, the gold criterion toward medical diagnosis for this condition is through histology. A liver biopsy preview demonstrates structure regarding the liver will look distorted accompanied by regenerative nodules, then enclosed by fibrous tissue. However, diagnosis for cirrhosis can be done without a liver biopsy exam, and simply making use of clinical findings. First, know that two clinical cirrhosis stages are categorized for the condition, the first being compensated, while decompensated cirrhosis the second type.
Compensated cirrhosis would be at the asymptomatic stage. Hence, the clinical diagnosis would be much more challenging to attain, then a liver biopsy may further be required. Second, for decompensated cirrhosis, it could be the symptomatic stage described as having the occurrence or growth of variceal hemorrhage, ascites, to hepatic encephalopathy. This makes diagnosis not as challenging. A liver biopsy may rarely be necessary, in fact.
Essential Recommendations
Cirrhosis should always be investigated among patients having chronic (less than 6 months in length) abnormalities found in liver enzymes, or as part of patients in which risk factors concerning cirrhosis can be found: obesity, alcoholic usage disorder, hepatitis B and C, metabolic syndrome (despite the lack of liver enzyme irregularities).
Tests listed below might help support cirrhosis diagnosis:
- Thorough physical examination
- Proper laboratory testing
- Proper imaging testing
- Liver stiffness measurement
Then again, physical examination, laboratory checks, as well as radiology tests (clinical results) can all generate entirely average results concerning an individual having compensated cirrhosis. More so, a liver biopsy (the invasive method) will be required for establishing (or excluding) cirrhosis diagnosis if you have higher suspicions and lack of non-invasive results.
Suggestive cirrhosis findings based on physical examination:
- Asterixis
- Ascites (a state of shifting dullness)
- Splenomegaly
- Wasting of the bi-temporal muscle
- A palpable left lobe associated with the liver (when you look at the epigastrium)
- Chronic liver’s disease stigmata (vascular spiders, palmar erythema)
- Abdominal collateral
- Tiny liver span (right lobe: the average is just around 9 cm)
Laboratory results implicative of cirrhosis:
- Platelet count is greater than 180,000
- Albumin < 3.8 mg/dL
- AST is less than ALT (for non-alcoholic etiology)
- INR is less than 1.2
- Bilirubin is less than 1.5 mg/dL
Imaging outcomes (MRI, abdominal ultrasound, CT scan) that is indicative of cirrhosis:
- Ascites
- Splenomegaly
- Nodular surface regarding the liver
- Collaterals
- Shrunk right lobe area in liver
- Enlarged left lobe are in liver
Diet and Nutrition
Once a patient has cirrhosis, he/she really need to consume a healthy and balanced diet. Best to always consult with the doctor, a nutritionist, to dietitian regarding healthier eating daily. Eliminate food and beverages that will damage the liver like alcohol or shellfish.
Treatment
Doctors would not be able to provide specified treatments that will cure cirrhosis. Nonetheless, they are able to treat a number of diseases that eventually cause cirrhosis. This is the reason why in the first few signs of having liver damage, patients need to consult their physician fast. Managing the root factors involving cirrhosis could keep the condition from becoming worse. More so, they may be able to, and can even help alleviate problems eventually leading to liver failure.
Clinical Trials
USA National Institute for Diabetes, Digestive & Kidney Disease (NIDDK), along with other parts among America’s National Institute for Health (NIH) carry out and promote research towards numerous diseases to conditions.
Your very own liver in fact is the biggest solid organ within your body. Your liver can help you by the process of the toxins out of the bloodstream. Moreover, your liver cleans blood which becomes enriched along with vitamins + minerals in the process of digestion. Be sure to always be mindful of what you eat or drink to better care for your liver and you will not have to expect any cirrhosis labs!