Liver cancer is a rare but serious condition that causes malignant cells to proliferate in liver tissue. If you have been diagnosed with liver cancer, you may be feeling confused and scared. Here we answer questions you may have surrounding your liver cancer diagnosis. Read on to find out more.
What Are the Different Types of Liver Cancer?
There are several different types of liver cancer, with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) being the most common form of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma. This form of cancer affects the hepatocytes, which are the primary type of cells present in the liver parenchyma.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: Cholangiocarcinoma or bile duct cancer is a form of cancer that affects the bile ducts. The bile ducts are small tubular structures that carry bile to and from the liver and play a role in digestion.
- Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma: This form of liver cancer is rare and tends to affect younger people. This form of hepatocellular carcinoma has different histological features when compared to the most common form of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Angiosarcoma: Angiosarcoma is a tumor that forms in the blood vessels. As a result, it can occur in many different parts of the body, including the blood vessels in the liver.
- Secondary liver cancer: The types of liver cancer described above are primary liver cancer, meaning that they originate in the liver. On the other hand, secondary liver cancer begins in another part of the body and spreads or metastasizes to liver tissue.
What Does Liver Cancer Diagnosis Look Like?
Many individuals with liver cancer are diagnosed during routine physical examinations and blood work, or during routine cancer screenings. Physicians use a variety of tests to detect the presence of cancer cells in the liver. Blood tests, medical imaging tests, and biopsy are important tools in the diagnosis of liver cancer.
- Blood tests: A sample of your blood may be taken to test for abnormalities in liver function and liver enzyme levels. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) levels may also be used as a diagnostic tool to detect the presence of an AFP-secreting liver tumor.
- Medical imaging: Medical imaging tests like ultrasounds, computed tomography (CT scans), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI scans) give physicians a picture of your liver. These medical imaging tests help reveal the presence of growths, liver tumors, and other abnormalities. Ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRI scans may also be used to determine whether liver cancer has metastasized to other areas of the body.
- Biopsy: A liver biopsy entails removing a small sample of liver tissue. The tissue sample is then analyzed in a laboratory for the presence of cancerous cells. A biopsy can help reveal the type of cancer and the stage of disease.
How Is Liver Cancer Treated?
If these tests reveal the presence of liver cancer, your team of doctors and healthcare providers will then work with you to go through your treatment options and form a cancer care and treatment plan. You will be treated at a cancer center by physicians specializing in oncology, and your treatment plan will be tailored to your specific needs. There are numerous treatment options that your healthcare team may suggest and administer, depending on the type of liver cancer you have and how progressed it is. The Mayo Clinic summarizes the possible treatments for liver cancer. (1)
Heating or Freezing Liver Cancer Cells
Extreme heat or cold can kill liver cancer cells. A doctor may perform heating or freezing procedures as part of your treatment. Microwaves or radio waves may be used to generate an electric current to target cancer cells. To cool cells, a cryoprobe is used to perform an ablation technique that delivers liquid nitrogen to cancer cells.
Surgical Removal
Surgical excision of the tumor and parts of the liver may be needed as part of your treatment. In some cases, the entire liver may need to be removed. If all liver tissue must be removed, then you will undergo a liver transplant. Liver transplantation entails replacing your liver with the healthy liver of a donor.
Chemotherapy or Radiation
Chemotherapy is a type of medication that is used to treat cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs destroy rapidly dividing cells, like those in cancerous growths. Chemotherapy medications may also be injected directly into a tumor. Radiation therapy, on the other hand, requires an external energy source to target cancerous growths like tumors.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the immune system to destroy liver cancer cells. Immunotherapy entails activating or altering the body’s natural immune system mechanisms to fight cancer growth.
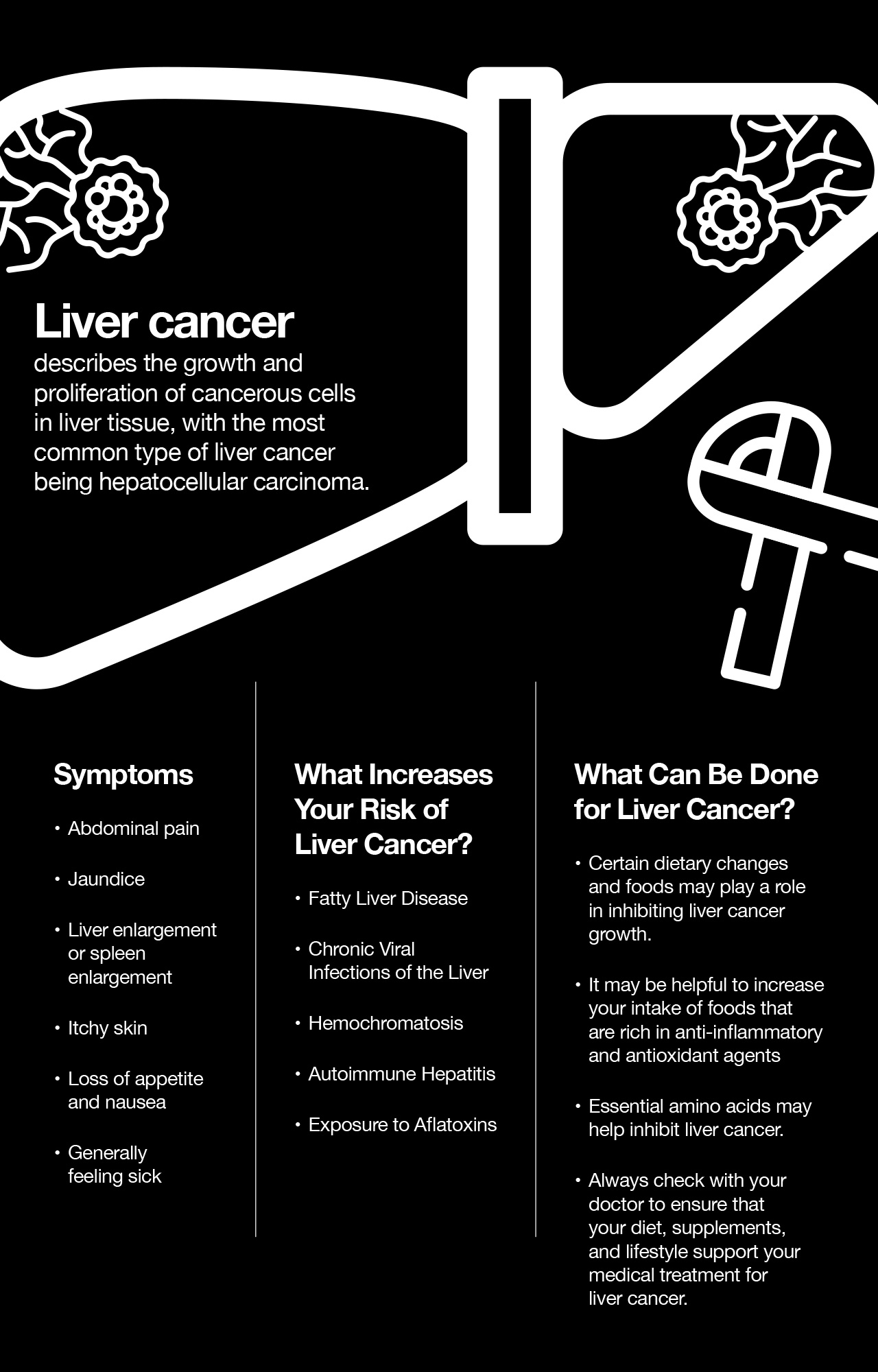
What Increases Your Risk of Liver Cancer?
Individuals with liver cancer often have other conditions that increase their risk of developing cancer. Here are some conditions that are connected to an elevated risk. If you’ve been diagnosed with liver cancer, you may have also had one of these risk factors.
Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is one of the most common liver conditions affecting American adults. Untreated and unresolved fatty liver disease increases the risk of developing liver cancer. Without intervention, fatty liver disease may progress to steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis, causing damage to healthy liver tissue. When liver cells are damaged repeatedly over time, the risk for liver cancer rises.
The chronic and excess consumption of alcohol over time is one cause of fatty liver disease. Alcohol is a toxin that increases oxidative stress and inflammation in all organ systems, including the liver. A western diet high in sugar and saturated fat is also linked to fatty liver disease. Both added sugars and saturated fat are known to interfere with healthy metabolic function, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease linked to diet is referred to as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Chronic Viral Infections of the Liver
Hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C are viruses that infect liver tissue. Hepatitis C is particularly common and can be spread through contaminated needles and contact with infected bodily fluids. A chronic hepatitis C infection results in liver inflammation and fat accumulation within the liver. Chronic viral infection damages liver tissue, which can lead to inflammation, fibrosis, and cirrhosis, ultimately increasing the likelihood of developing liver cancer.
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a genetic condition that causes the body to absorb excess iron. Iron may then accumulate in different areas of the body, such as the joints, heart, and liver. Excess iron in the liver can cause liver inflammation and fatty liver disease, over time causing damage.
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis describes the immune system mischaracterizing healthy liver tissue as a threat, and therefore launching an attack. A hyperactive immune system then begins attacking and damaging liver tissue. Over time, autoimmune hepatitis can increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
Exposure to Aflatoxins
A type of mold called Aspergillus flavus is responsible for producing toxic compounds called aflatoxins. Aflatoxins sometimes grow on grains that haven’t been stored correctly. Exposure to high levels of aflatoxins causes liver damage and increases your risk of developing liver cancer.
What Are the Symptoms of Liver Cancer?
Symptoms and signs of liver cancer may not be present in early stages of the disease. However, as liver cancer affects more of your liver tissue, you will likely experience symptoms that mimic those of other types of advanced liver disease. Liver cancer symptoms may include:
- Abdominal pain: Pain in the abdomen may be a sign of liver cancer. You may experience pain on the right side, in the upper quadrant of the abdomen. You may also experience pain in the right shoulder blade.
- Jaundice: Jaundice describes yellowing of the skin as a result of bilirubin accumulation. Bilirubin is a byproduct of red blood cell degradation. Normally, the liver processes bilirubin. However, when the liver is damaged by cancer growth, it is unable to clear bilirubin from the bloodstream.
- Liver enlargement or spleen enlargement: Liver cancer can be linked to an enlarged liver or spleen. As a result, you may feel heaviness or swollen on the upper right or left quadrant of the abdomen.
- Itchy skin: When the liver isn’t functioning properly, bile salts may build up beneath the skin and cause itching.
- Loss of appetite and nausea: Liver cancer is often accompanied by gastrointestinal symptoms, such as fullness after a small meal, loss of appetite, and nausea. You may also experience unintended weight loss.
- Generally feeling sick: If you have liver cancer, you may feel low energy and exhausted. The liver plays a critical role in so many biological mechanisms, so when it’s not working as it should, the body doesn’t function properly, leading to fatigue and exhaustion.
What Can Be Done for Liver Cancer?
Moreover, mounting evidence suggests that certain dietary changes and foods may play a role in inhibiting liver cancer growth. For example, a review published in Nutrients explores the research showing the liver-protective and cancer-inhibiting effects of certain foods, such as pomegranates, plums, asparagus, and garlic. (2)
It may be helpful to increase your intake of foods that are rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agents, which may play a role in slowing cancer. Fruits, veggies, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and soy products are nutrient-rich foods that may support liver health.
Essential amino acids are other compounds found in food that may help inhibit liver cancer. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein, and research shows that certain amino acids may help support liver health. (3) A study published in Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology shows that certain essential amino acids like branched-chain amino acids may help inhibit cancer proliferation. (4)
Because eating high-protein foods may be difficult to stomach while enduring cancer treatment, supplementation may be a better route for ensuring you’re getting the optimal ratios of essential amino acids that you need. Always check with your doctor to ensure that your diet, supplements, and lifestyle support your medical treatment for liver cancer.
Additionally, it’s also best to eliminate alcohol when you have liver cancer. Introducing more toxins to the body puts more stress on the liver and causes more damage. Plus, alcohol may interact negatively with cancer treatments, worsening side effects and affecting efficacy.
What Is the Prognosis for Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer is a serious disease. The prognosis for liver cancer depends largely on how early the cancer is diagnosed, whether it has spread, and what stage it is. The American Cancer Society gives the relative survival rate 5 years after diagnosis to be 30%. (5) This means that compared to the survival rates of individuals without liver cancer, individuals with liver cancer are 30% as likely to survive for 5 or more years after diagnosis. (5)
Conclusion: Liver Cancer Diagnosis and What You Should Know
Liver cancer describes the growth and proliferation of cancerous cells in liver tissue, with the most common type of liver cancer being hepatocellular carcinoma. Your healthcare team including oncologists and radiologists will devise a liver cancer treatment plan to tackle your specific case. Treatment options may include procedures like surgery, heating or cooling of the cancer cells, radiation, or chemotherapy. In addition, eating a healthy, balanced diet and avoiding alcohol may play a role in discouraging liver cancer growth.
References:
(1) https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/liver-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353664
(2) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4808884/
(3) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6619856/
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6088198/
(5) https://www.cancer.org/cancer/liver-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html